Customer Experience
Your path to the digital customer portal—in 7 steps
Today’s customers expect fast self-service and complete transparency. A customer portal offers exactly that – and more! Learn how to optimize your processes, retain customers, and lay the foundation for digital sales in seven steps.
A contribution by Benjamin Rost, Member of the Executive Board
Published: 14/04/2025
Reading time: 11.4 Min
Contents
What is a customer portal?
When talking about a digital customer portal, many companies refer to a web shop. However, a customer portal is an interesting addition or “replacement” for the classic e-commerce solution. But what exactly is a customer portal? A customer portal is a digital access point that enables your customers and prospects to independently carry out a variety of actions with your company. And that’s around the clock!
The customer portal serves as an interface between your company and your customers and provides functions that enable them to browse products, request quotes, check order status, access invoices, and submit support requests.
Through personalization and constant availability, the customer portal creates an improved customer experience that increases customer satisfaction and loyalty. It also provides valuable insights by collecting user data that can be used to further develop your own business strategy and helps reduce operating costs by increasing efficiency and automating frequent customer inquiries.
Digital Experience Platform
A customer portal, also known as a DXP, is a customer-centric platform that integrates all channels, content, and functions.
Depending on the business model and requirements, it can combine e-commerce, PIM, CMS, and AI components to ensure a high-quality and consistent customer experience.
In short: The customer portal is the digital interface between your company and your customers!
55 %
of e-commerce managers invest in a digital customer portal.
Source: E-book “The added value of a digital customer portal from a business perspective” by Intershop
55 %
of e-commerce managers invest in a digital customer portal.
Source: E-book “The added value of a digital customer portal from a business perspective” by Intershop
Typical challenges for companies
Even though direct interaction with people plays an important role, especially in B2B, the lack of a customer portal leads to many negative aspects in the relationship between your company and your customers. Your customers certainly appreciate transparency and direct access to information. A customer portal provides both. If this is missing, however, customers always have to pick up the phone and obtain information by telephone, for example. This costs your customers time, but it also generates process costs for you that can be avoided. The interaction and relationship between customer and company is also negatively affected by a lack of self-service. Time is of the essence, even for your customers. Direct self-service access to invoices and documents is becoming increasingly important. Young buyers in particular choose suppliers based on these criteria.
Reasons for a customer portal
A customer portal can help you solve many challenges at once. Similar to how a web shop digitizes transactions, the customer portal helps you digitize the relationship between your field service, office staff, customer support, and your customers.
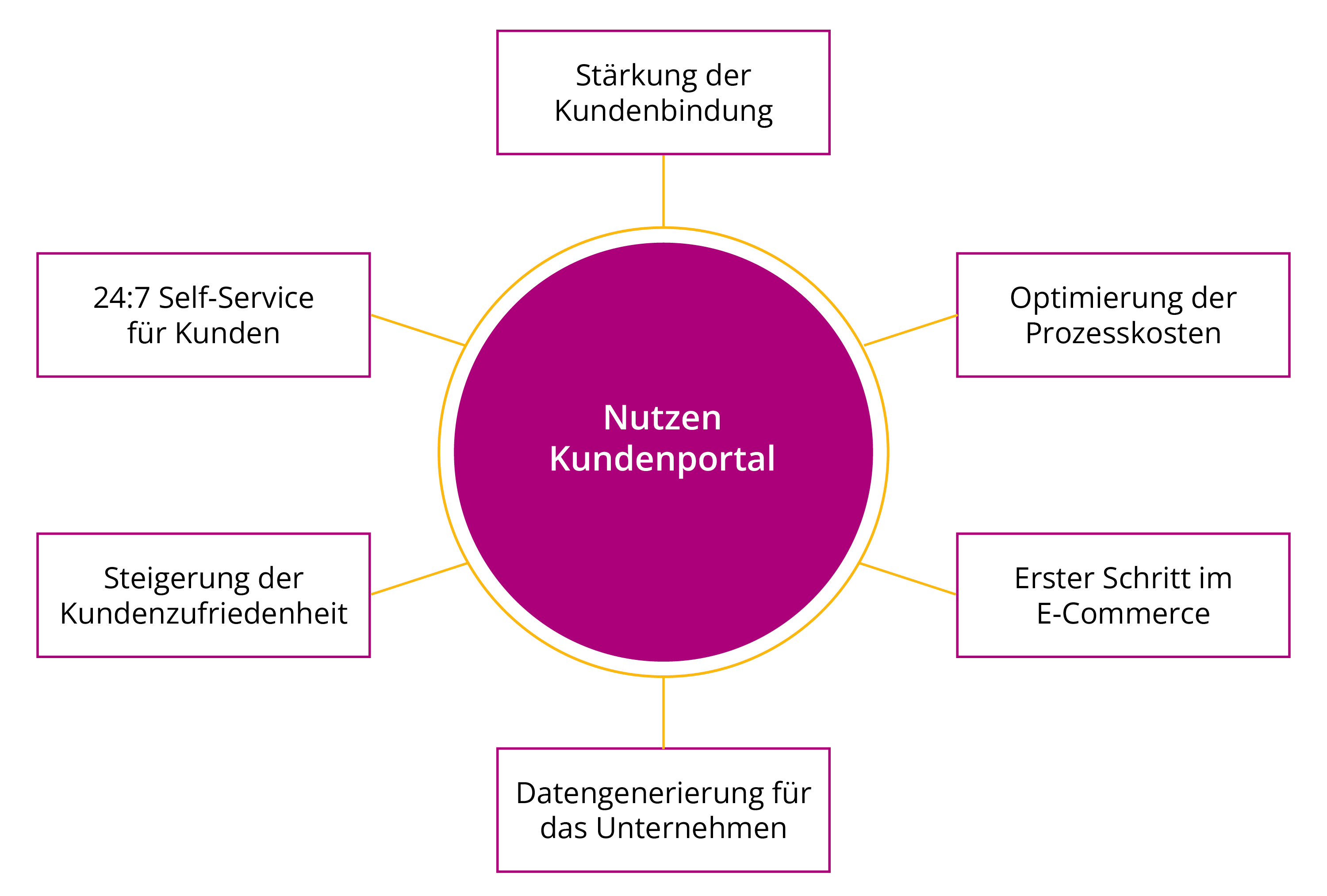
process optimization: A customer portal can automate time-consuming manual processes such as order processing, data management, and customer communication. This means that orders and service requests can be received and processed around the clock without human intervention. This increase in efficiency leads to faster processing times and minimizes sources of error, as data is entered directly by the customer and transferred to the internal system.
relief for sales: Customer portals serve as the first point of contact for customers, which means that standard inquiries and simple transactions no longer have to be handled by the sales department. This allows sales staff to focus their time and attention on more demanding tasks, such as providing personal advice on complex issues, relationship management, or acquiring new customers. This reduction in workload can increase job satisfaction, as employees have to spend less time on routine inquiries and have more time for value-adding activities.
Erhöhung des Ersatzteilgeschäfts: A customer portal gives customers direct access to a wide range of spare parts and accessories. Intuitive search functions, detailed product information, and simple ordering processes encourage self-service and can increase order frequency and quantity. The portal also enables cross-selling and up-selling, as it can display relevant additional products to customers based on their purchasing behavior. This allows customers to find and order spare parts with minimal effort, which strengthens customer loyalty and helps the company achieve stable, recurring sales.
Main components of a customer portal
The core components of a customer portal can vary depending on the business area and industry, but there are some basic functions that are often essential for an effective and customer-oriented portal:

As with a web shop or e-commerce platform, you need features and processes that deliver added value to your customers and employees.
Customer portal as an entry point to e-commerce
A customer portal is a suitable entry-level project for e-commerce. Even if you don’t currently see any benefit in e-commerce or are unable to enter the digital sales market, a customer portal can serve as a potential basis for digitizing transactions in the future.
First digital experience: A customer portal offers an uncomplicated way to gain initial digital experience. It can facilitate the introduction of online interactions and prepare customers and companies for full e-commerce.
Introduction to online transactions: By providing functions such as ordering and payment, customers and companies become accustomed to the process of online transactions.
Customer loyalty and feedback: The portal opens up direct communication channels for feedback and customer loyalty—a critical element for success in e-commerce.
Establishing an online presence: Before a comprehensive online store is established, the portal enables the development of an online presence and strengthens the brand image in the digital space.
Showcase for products/services: The portal can function as a digital showcase where customers can explore the product range and learn about products and services.
Collecting data and insights: The data collected through the portal provides important insights into customer behavior and preferences, which are crucial for optimizing future online sales.
Amortization of a customer porta
It is difficult to give a general answer to the question of how much investment a customer portal requires. It depends largely on the range of functions, interfaces, and integration into the company’s own system landscape.
However, compared to a web shop, a “reasonable” investment volume can be easily derived from potential process savings. The question of budget therefore often depends on the question of potential savings.

investment blocks
- Development/implementation
- Platform & infrastructure
- Interfaces and integration
- Maintenance and updates
- Training and introduction
- Marketing and launch
Realistically, companies should prepare a detailed financial forecast, paying attention not only to immediate costs but also to long-term economic effects. A customer portal should be viewed as a strategic investment that contributes indirectly to business success in addition to direct financial returns.
To estimate the payback period, it is useful to conduct a detailed cost-benefit analysis, which may also include a return on investment (ROI) calculator. It is important to consider both quantitative (e.g., increased sales figures) and qualitative benefits (e.g., increased customer satisfaction). Companies should not only consider the immediate costs, but also the long-term financial implications.
Increase in sales:
Does the portal open up new income streams or encourage purchases of additional products?
Efficiency improvements:
How much does the company save in process costs through automation and reduced staffing?
Competitive advantages:
Does the portal give the company an advantage over its competitors that could translate into a gain in market share?
A customer portal should be viewed as a strategic investment that contributes indirectly to business success in addition to direct financial returns.
The 7 steps to a customer portal
01
Needs analysis and goal definition:
Before introducing a customer portal, it is crucial to carefully analyze the specific needs of users and the business objectives of the company. This includes determining the core functions of the portal, creating user profiles, and defining how the portal should improve the customer experience and contribute to increasing sales.
02
Selecting the right technology platform:
Based on the above analysis, a suitable technology platform must be selected. The platform should be scalable, secure, and compatible with existing enterprise systems such as CRM (customer relationship management) or ERP (enterprise resource planning). A user-friendly interface for customers and the ability to customize the portal to the specific needs of the company are also important.
03
Data integration and security:
One of the critical aspects is the integration of existing customer data into the new portal to ensure a seamless user experience. Interfaces must be created to enable smooth data flow between the portal and other enterprise systems. At the same time, a high standard of data security must be ensured to protect sensitive customer information and meet compliance requirements.
04
Development of a clear role and authorization structure:
It must be precisely defined which information and functions are available to the different user types within the portal. This includes creating access policies and implementing authorization levels to ensure that users can only access the areas and data intended for them.
05
Design and user experience (UX).
The design of the portal should be carefully planned from both a visual and functional perspective. The user experience should be intuitive to ensure high user acceptance and satisfaction. User studies can be conducted here to meet the expectations of the target group.
06
Development and integration:
The next step is to develop the portal based on the requirements and objectives. This includes both front-end and back-end development. Integrations into existing IT landscapes such as CRM software and ERP systems to ensure a seamless flow of information and functionality.
07
Test and feedback cycles:
Vor dem offiziellen Launch müssen ausgiebige Tests des Kundenportals unter realen Bedingungen stattfinden, um technische Fehler zu identifizieren und zu beheben. Außerdem sind die Rückmeldungen von Pilotnutzern wertvoll, um die Nutzerfreundlichkeit und Funktionalität des Portals zu bewerten und gegebenenfalls zu optimieren. Dieser iterative Prozess hilft dabei, ein robustes und anwenderfreundliches Endprodukt zu schaffen, das die Akzeptanz bei den Zielkunden erhöht.
Are you interested?
Let’s talk.